Authors¶
Feng Zhu
and Deborah Khider
Preamble¶
Variations in solar irradiance have been hypothesized to be responsible for part of the variability in global mean surface temperature (GMST) over the Common Era (the last 2,000 years or so). In this notebook we use Pyleoclim to test this hypothesis using wavelet transform coherency between reconstructions of solar irradiance and GMST.
This notebook reproduces Fig S16of PAGES2k Consortium manuscript entitled “Consistent multidecadal variability in global temperature reconstructions and simulations over the Common Era”.
Technical Skills Involved:
Loading data using pandas
Applying and interpreting Wavelet Transform Coherency analysis
Data¶
Reconstruction of solar irradiance:SATIRE-H dataset (Vieira et al. 2011), as compiled by Barboza et al. (2020). GMST: Ensemble of Neukom et al (2019), who applied 7 different statistical methods to the PAGES 2k database.
Reading time¶
5 min
Keyword¶
Pyleoclim; Coherence Analyis; Common Era; Solar irradiance
Let’s load the necessary packages:
# load packages
import pyleoclim as pyleo
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import os
from matplotlib import gridspec
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tqdm import tqdmExploratory Data Analysis¶
Let’s start by opening the forcing data and GMST reconstruction:
database_path = '../data/'
forcing_filename = 'Neukom2019_forcing.csv'
GMST_filename = 'Neukom2019_GMST_recon_medians_selection.txt'
forcing_df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(database_path, forcing_filename))
GMST_df = pd.read_table(os.path.join(database_path, GMST_filename))display(GMST_df.head())display(forcing_df.head())Let’s import this information into Pyleoclim and plot the corresponding timeseries:
ts_solar = pyleo.Series(time=GMST_df['Year'].values,
value=forcing_df['solar'].values,
label='Total Solar Irradiance',
time_name='Year',
time_unit='CE',
value_name='TSI',
value_unit=r'W m$^{-2}$')
Time axis values sorted in ascending order
exp_names = list(GMST_df.columns.values)[1:]
ts = {}
for i, exp in enumerate(exp_names):
ts[exp] = pyleo.Series(time=GMST_df['Year'].values,
value=GMST_df[exp].values,
label=exp,
time_name='Year',
time_unit='CE',
value_name='T anomaly',
value_unit='K')Time axis values sorted in ascending order
Time axis values sorted in ascending order
Time axis values sorted in ascending order
Time axis values sorted in ascending order
Time axis values sorted in ascending order
Time axis values sorted in ascending order
Time axis values sorted in ascending order
pyleo.set_style('web')
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(4, 1)
gs.update(wspace=0, hspace=0)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=[10, 6])
ax1 = plt.subplot(gs[0:3, :])
for i, exp in enumerate(exp_names):
ts[exp].plot(ax=ax1,linewidth=1)
ax1.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1.0), loc='upper right')
ax2 = plt.subplot(gs[3, :], sharex=ax1)
ts_solar.plot(ax=ax2, linestyle='--', linewidth=3, color='black')
ax2.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.21, 1.0), loc='upper right')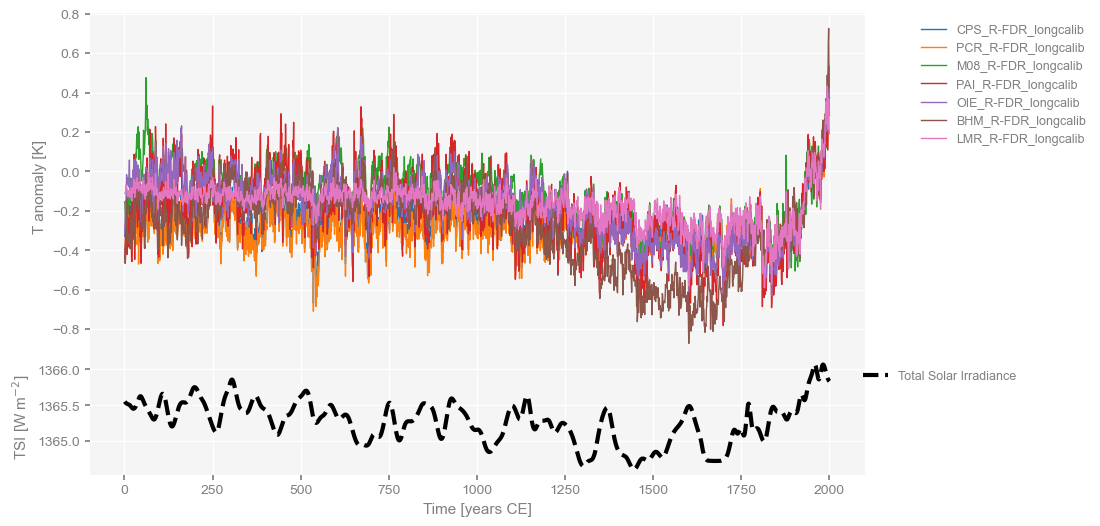
Wavelet coherency analysis¶
This uses Pyleoclim’s wavelet coherence method. Since the series are evenly-spaced, we will use the CWT method.
scale = np.logspace(1, 11, num=51, base=2)
freq = 1/scale[::-1]
col = {}
for exp in tqdm(exp_names):
print('Evaluating coherence with '+ exp +'\n')
col[exp] = ts_solar.wavelet_coherence(ts[exp],
settings={'freq':freq}).signif_test(number=200, mute_pbar=True) 0%| | 0/7 [00:00<?, ?it/s]Evaluating coherence with CPS_R-FDR_longcalib
14%|█▍ | 1/7 [00:09<00:55, 9.17s/it]Evaluating coherence with PCR_R-FDR_longcalib
29%|██▊ | 2/7 [00:18<00:46, 9.36s/it]Evaluating coherence with M08_R-FDR_longcalib
43%|████▎ | 3/7 [00:28<00:37, 9.45s/it]Evaluating coherence with PAI_R-FDR_longcalib
57%|█████▋ | 4/7 [00:38<00:28, 9.59s/it]Evaluating coherence with OIE_R-FDR_longcalib
71%|███████▏ | 5/7 [00:47<00:19, 9.67s/it]Evaluating coherence with BHM_R-FDR_longcalib
86%|████████▌ | 6/7 [00:57<00:09, 9.77s/it]Evaluating coherence with LMR_R-FDR_longcalib
100%|██████████| 7/7 [01:07<00:00, 9.60s/it]
We can now plot the results for each reconstruction. Colors indicate the level of coherency, while arrows show the phase angle (right = 0°, left = 180°, top = 90°, bottom = 270°, with intermediate directions representing angles in between).
period_ticks = np.logspace(1, 11, num=11, base=2)
for exp in exp_names:
fig, ax = col[exp].plot(yticks=period_ticks)
ax.set_title(exp, fontweight='bold')
pyleo.closefig()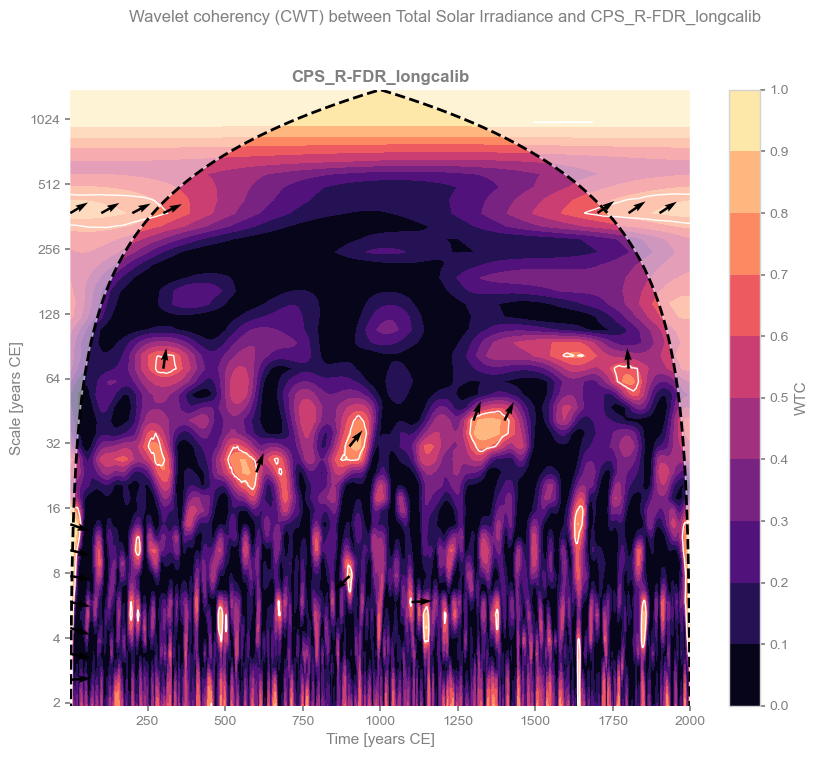
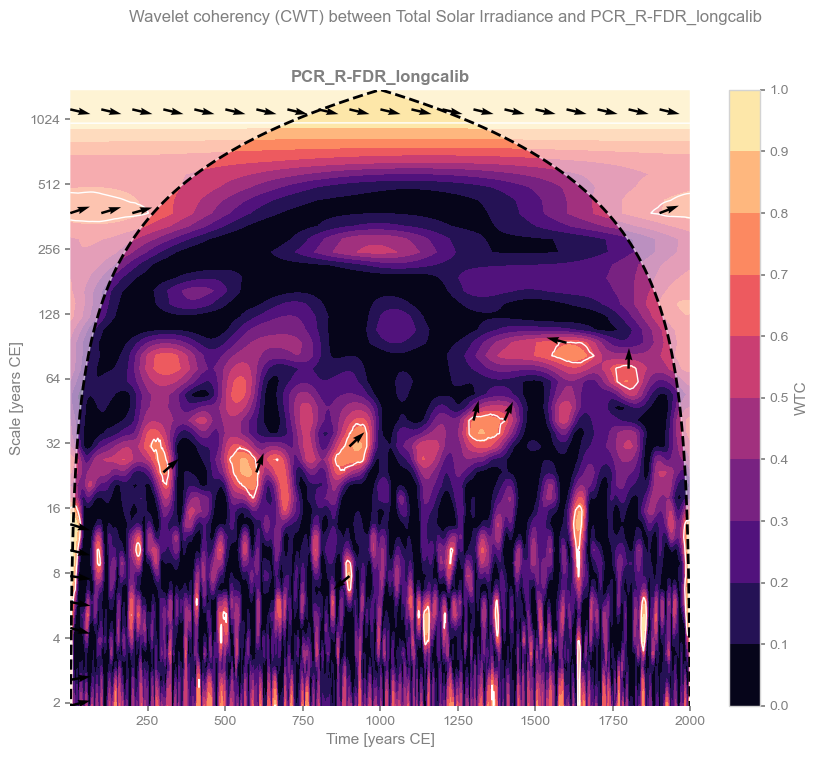
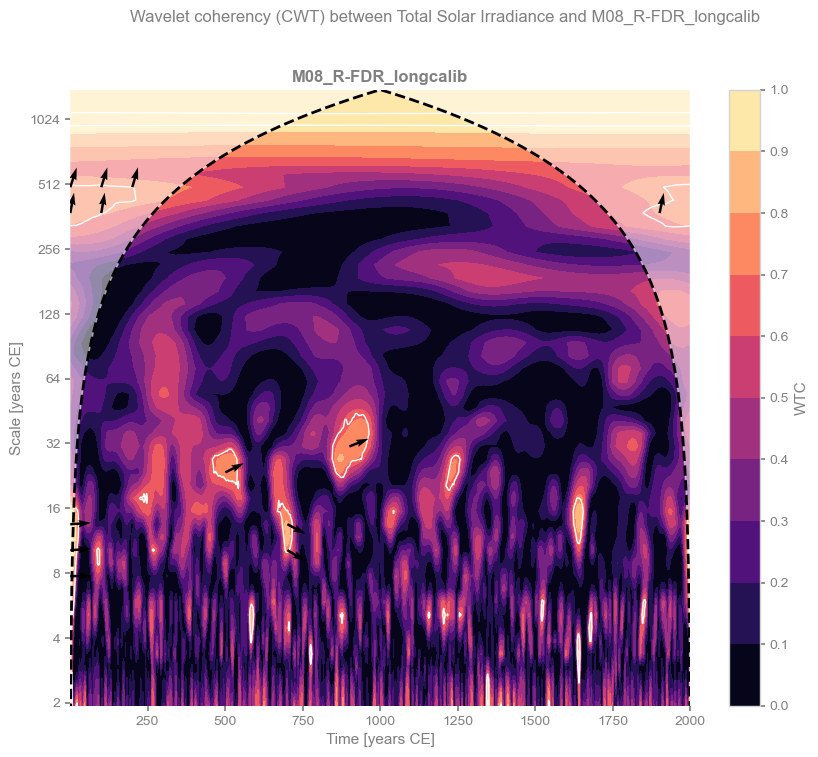
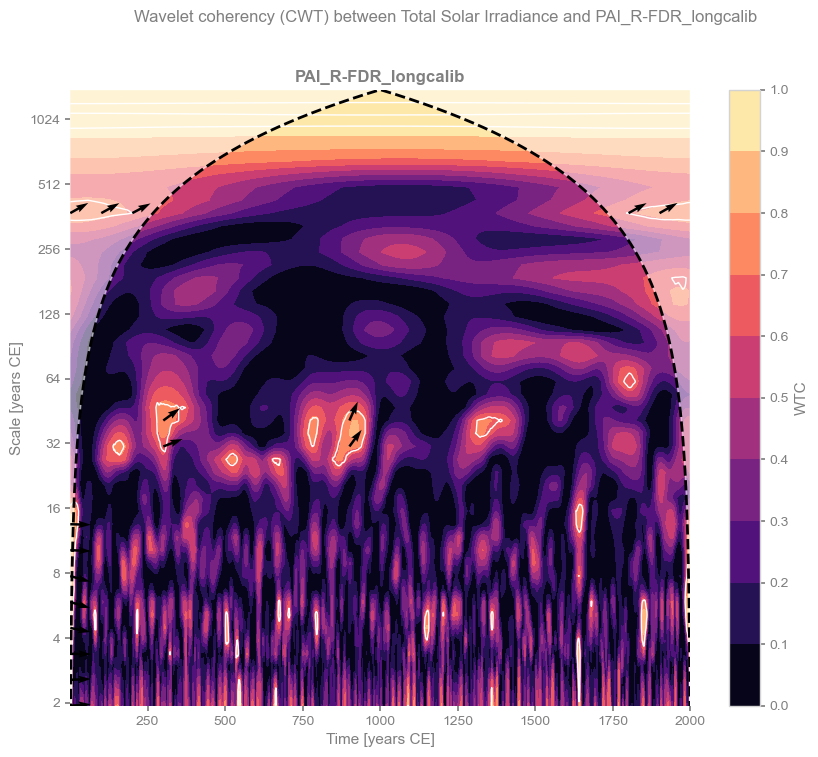
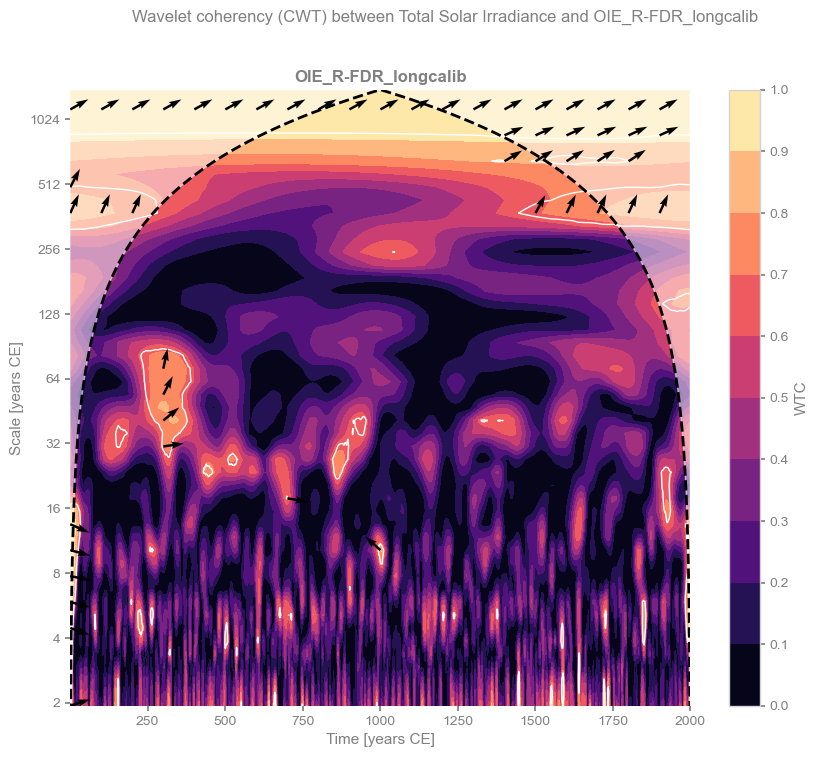
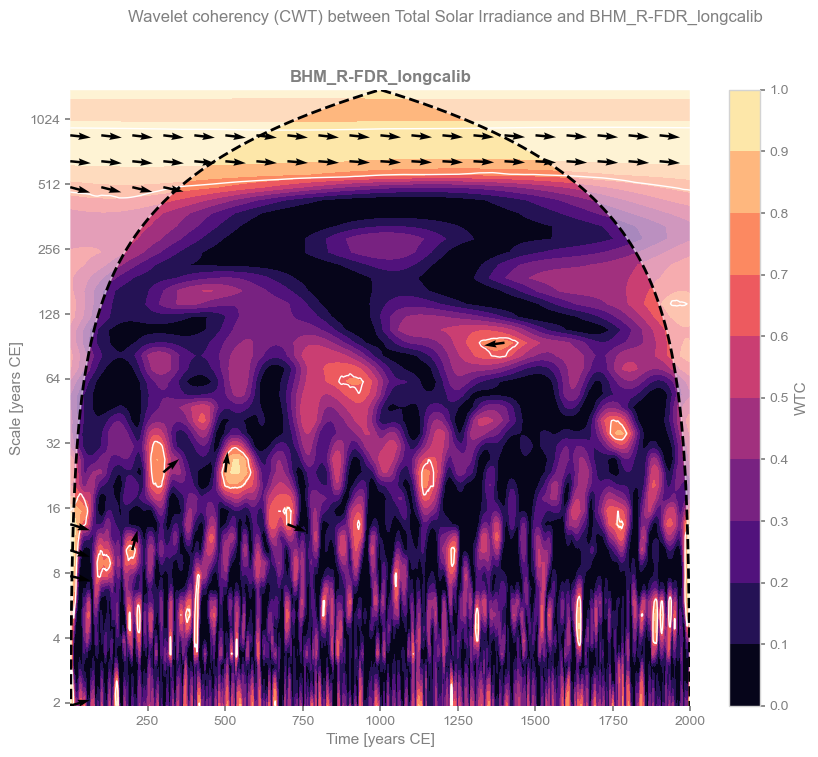
In some cases, there is a hint of an in-phase relationship (high coherency and phase angles close to 0°) at periods longer than 500 years. However, this signal lies near the cone of influence (the region of the scalogram affected by edge effects) and does not appear significant when tested against a red-noise (AR(1)) benchmark. The main exception is the BHM reconstruction from Barboza et al. (2019), which explicitly includes solar forcing as a predictor. It is therefore unsurprising that this reconstruction shows coherence with solar variability, although the original study demonstrates that the signal is weak. Overall, we find no evidence for a robust solar influence on climate in these reconstructions.
- Vieira, L. E. A., Solanki, S. K., Krivova, N. A., & Usoskin, I. (2011). Evolution of the solar irradiance during the Holocene. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 531, A6. 10.1051/0004-6361/201015843
- Barboza, L. A., Emile-Geay, J., Li, B., & He, W. (2019). Efficient Reconstructions of Common Era Climate via Integrated Nested Laplace Approximations. Journal of Agricultural, Biological and Environmental Statistics, 24(3), 535–554. 10.1007/s13253-019-00372-4
- Neukom, R., Barboza, L. A., Erb, M. P., Shi, F., Emile-Geay, J., Evans, M. N., Franke, J., Kaufman, D. S., Lücke, L., Rehfeld, K., Schurer, A., Zhu, F., Brönnimann, S., Hakim, G. J., Henley, B. J., Ljungqvist, F. C., McKay, N., Valler, V., & von Gunten, L. (2019). Consistent multidecadal variability in global temperature reconstructions and simulations over the Common Era. Nature Geoscience, 12(8), 643–649. 10.1038/s41561-019-0400-0
- Emile-Geay, J., McKay, N. P., Kaufman, D. S., von Gunten, L., Wang, J., Anchukaitis, K. J., Abram, N. J., Addison, J. A., Curran, M. A. J., Evans, M. N., Henley, B. J., Hao, Z., Martrat, B., McGregor, H. V., Neukom, R., Pederson, G. T., Stenni, B., Thirumalai, K., Werner, J. P., … Zinke, J. (2017). A global multiproxy database for temperature reconstructions of the Common Era. Scientific Data, 4(1). 10.1038/sdata.2017.88